World History
last updated 8 Mar 2019
Upper Middle Lower
Under Construction 
History of Man
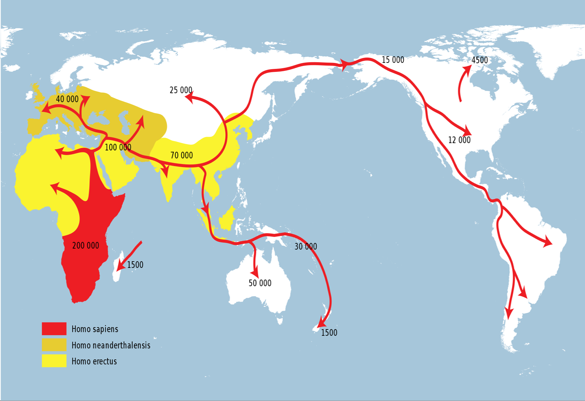
Note: There doesn't seem to be much agreement on dates and names for different eras. Modern history books have gotten away from these classifications. See below.
| Dates | Area | Culture |
|---|
| | Prehistoric Era 2 MYA - 4000 BCE | |
|---|
Paleolithic
(Old Stone Age) |  |
2 M - 250,000 YA - Stone chopping tools (Mode 1 and 2)
1.6-2.4 Mya Homo Genus
(
MYA - Million yrs ago, Kya - 1,000 years ago)
800,000 - Harnessing of fire
| Stone Age |
80,000-300,000 BCE Archaic Homo Sapiens
430,000 Neanderthals in Europe (uncertain classification) |
 |
Smaller flake tools (mode 3)
One innovaion per 20,000 years ‡ | Population ?
500,000 - 100,000 BCE - brains grow at a rapid rate |
300,000 BCE Modern Homo Sapiens
150,000-50,000 language developed.
|
 |
Full behavioral modernity - 50,000 BCE
Stone blade making technology (mode 4), bone and ivory implements (e.g. needle), decorative items
38,000 BCE First art - Caves in Europe, Asia, Africa and Australia.
One innovaion per 1,400 years ‡ | Population c. 3 Million |
15-8,000 BCE First settlement in fixed communities
Gobekli Tepe: The World's First Temple?
First postholes at Stonehenge | |
Mesolithic *
10,000-
6,000 BCE | End of Ice age
Transition period from hunter-gathering to agriculture.
9,000 BCE Cultivation of grains in proto-city of Jerico
5,300 BCE Cities of Sumeria
One innovaion per 200 years ‡ | Population c. 4 Million |
Neolithic *
6,000-
2,200 BCE | 4,000 BCE A change from a nomadic way of life to a sedentary lifestyle.
he Neolithic farmers began to build permanent settlements and, by using fire and more advanced stone tools like polished stone axes, began the deforestation of large sections of land for the planting of crops.
Invention of the wheel. | Copper Age |
|
Ancient Era (Primeval) Period 2-4000 BCE - 440 CE †
|
3,500 BCE - Written Language starting with Sumerian cuneiform
Stonehenge |
5,000-220 BCE - Early China/Japan
Yangshao, Longsham, Xia, Shang, Zhou
prior to 3,000 BCE - Andean civilizations build sophisticated temple architecture in Peru |
| 3,500 BCE Domestication of the horse |
| Egyptian Pyramids |
3,200-400 BCE - Mesopotamia:
Assyrians, Sumerians, Babylonians (Hammurabi, 1800 B.C.)
Population 25 - 100 Million
| Bronze Age *
3,300-1,200
BCE Asia
3,200-750
BCE Europe |
| 3,200 - 30 BCE - Egypt |
| 1193-1184 BCE - Trojan Wars | Iron Age |
| 1000 BCE-300 CE - Classical Traditions, Major Religions and Giant Empires
|
1028 BCE - Israel united under Saul and David
prior to 1,000 BCE - Burial mounds in Ohio Valley
900 BCE - Hebrew Language developed
900 BCE - Chávin de Huántar Andean Civilization in Norte Chico region of Peru
800 BCE - Latin Language developed
700-600 BCE - Mayan civilization in Central America
|
Classical Antiquity
597 BCE Babylonians (Nebuchadnezzar) capture Jerusalem
Hebrew scriptures written down in exile.
539 Cyrus II of Persia invades and conquers Babylon
530 Buddha, Confucius
585 - 250 Greece (Socrates [399], Hippocrates [370], Plato [347], Aristotle [322], Euclid [300])
336 BC - Alexander the Great, King of Macedonia captures Persian empire
509 BC - 27 BC Roman Republic (mixture of democracy and oligarchy)
200 BC - 700 AD - Teotihuacan Mesoamerican civilication Mexico.
200 BC Nazca and Mochica Andean Civilizations in South America
27 BC - 476 AD Roman Empire (ruled by a single Emperor)
30 AD - Death of Christ
312 - Constantine I, Roman Emperor, adopts Christianity
Population 200-300 Million
| |
Middle Ages - High Medieval Era 400-1,500 AD
|
| | Medieval † |
330-1453 Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire)
(St. Augustine 354-430 - Carthage) |
| 350-550 Huns (Mongols) capture land from central Asia to modern Germany |
| 632 Death of Mohammed |
711-1085 Moorish (Muslim) rule of Toledo, Spain
during a golden age of religious tolerance, science and culture. |
| 1015-1295 Crusades |
1066 Norman Invasion of England- William the Conqueror
| | 1000-1200 | Native American Pueblos Taos, NM |
| Native American Cliff Dwellers Mesa Verde, Co |
| 1300's |
Start of Renaissance in Tuscany | Renaissance |
| 1400-1550 | Age of exploration |
| 1439 | Gutenberg invented the Printing Press |
| 1450 | Machu Picchu Inca Estate |
Modern Era |
| 1500-1550 | Leonardo da Vinci [1452-1519] and Michelangelo |
| 1500-1598 | The Reformation (Luther [1483-1546], Calvin [1509-1564])
Population 500 Million |
| 1540-1688 | The Scientific Revolution
Copernicus (1473-1543) Galileo (1564-1642)
Francis Bacon (1561-1626)
William Shakespeare (1564-1616) |
| 1560-1700 | Spanish Inquisition (1478-1834) |
| 1650-1700 | Baroque
Start of Enlightenment
Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750) | Enlightenment |
| 1600-1747 |
René Descartes (1596-1650)
Rembrandt (1606-1669)
Blaise Pascal (1623-1662)
John Locke (1632-1704)
Isaac Newton (1643-1747)
|
| 1700-1850 | Industrial Revolution |
| 1750-1800 | Classical Period in Music
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart 1756-1791, Haydn (1732 -1809)
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827) [later works are Romantic] |
| 1790-Present | Late Modern | High Modern |
|---|
| 1800-1900 | Romantic period in music (1800-) and literature (1750-)
Population 960 Million - 1.6 Billion
|
| 1859 | "The Origin of Species" - Charles Darwin |
| 1865 | "Experiments on Plant Hybridization" - Gregor Mendel |
| 1870 |
Invention of the telephone - Alexander Graham Bell |
| 1869-1948 | Mahatma Gandhi
|
| 1900 | Sigmund Freud's books on psychoanalysis |
| 1907-1915 | General relativity - Albert Einstein |
|
PostModern
|
| 1948- | Postmodern art and architecture |
| 1980- | Postmodern philosophy |
Mya - Million years ago
Kya - Thousand years ago
1. Dates for the Paleolithic age are based on stone tool types and vary by location:
Mya - Million Years ago, BP - Before Present
- Lower 2.5 Mya - 300,000 | 2,5 Mya - 200,000 BP
- Middle - 300,000-30,000 | European 150,000- 35,000
- Upper: 40,000-10,000 | 100,000 - 11,000
In the 2nd edition of World Prehistory, 1969, Grahame Clarke envisioned an evolutionary progression of flint-knapping in which the "dominant lithic (stone tool making) technologies" occurred in a fixed sequence from Mode 1 through Mode 5.
* Dates for the Bronze and Iron age as well as the Mesolithic and Neolithic periods vary from society to society.
The Iron age begins in the 12th century BC in the ancient Near East, and ancient Greece, the 8th century BC in Central Europe and the 6th century BC in Northern Europe.
In some areas of the world the Bronze Age followed the Neolithic age. On the other hand, in many parts of sub-Saharan Africa, the Neolithic age is directly followed by the Iron Age.
In some places there was a copper age between the Stone and Bronze ages.
Bronze is made of copper and tin. Bronze and tin are relatively easy to extract from ore, whereas iron ore requires a much more energy intensive and complicated process to smelt.
With the collapse of the Bronze Age around 1200 B.C.E. trade networks fell apart and metallurgists could not get tin and began to work with iron.
See
Iron vs. Bronze: History of Metallurgy - education-portal.com Video
† - There doesn't seem to be general agreement on Era's:
Modern history books have gotten away from using these classifications, possibly because dates vary from civilization to civilization.
Some include Medieval and Industrial periods as Eras and some don't.
Ancient: 2,000 BCE - 1,000 | CE, 3,110 BCE - 500 CE | 4,000 BEC - 8 BCE
Medieval: 1000 - 1600 | 600-1,500
Modern: 1500- | 1,600-
Industrial Era: 1750-1850
These eras of man are different from the geological eras. We are in the
Cenozoic gelogical era (65 Mya - today), Quaternary Period (1.8 Mya).
Pleistocene Epoch 1.8 Mya - 11,000 bp, Holocene Epoch 11,000 years ago - today.
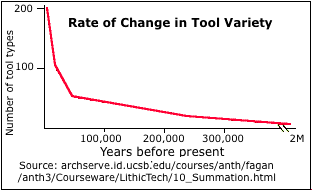 ‡ - In Robert Wright's 2000 book "Nonzero:", he makes the point for innovation as a function of population density.
‡ - In Robert Wright's 2000 book "Nonzero:", he makes the point for innovation as a function of population density.
The paper "Cultural Innovations and Demographic Change", Human Biology - Volume 81, Numbers 2-3, April-June 2009, by Peter J. Richerson et. al. Department of Environmental Science and Policy, UC Davis, states "Demography plays a large role in cultural evolution through its effects on the effective rate of innovation."
|
 History
History
 World History
World History
 History
History
 World History
World History

