Links
Optical Telegraphy:
Early communications consisted of smoke signals in Africa, the Americas and parts of Asia. In the 1790s, the first fixed semaphore systems emerged in Europe; however it was not until the 1830s that electrical telecommunication systems started to appear.
Electrical Telegraph:
Experiments on communication with electricity, initially unsuccessful, started in about 1726. Scientists including Laplace, Ampère, and Gauss were involved.
In 1844 Samuel Morse patented the modern telegraph
by 1851 telegraph lines in the United States spanned over 20,000 miles (32,000 kilometres). Morse's most important technical contribution to this telegraph was the simple and highly efficient Morse Code, co-developed with Alfred Vail,
Telephone service - Bell Telephone and AT&T:
Bell Telephone Company was organized in Boston, Massachusetts on July 9, 1877 based on Alexander Graham Bell's invention. Theodore Vail, cousin of Alfred Vail became the general manager of the American Bell Telephone Company in 1878.
Ownership of American Bell was transferred to its own subsidiary, American Telephone & Telegraph Company (AT&T Company)in 1899.
In 1907, Theodore Newton Vail became President of AT&T. Vail believed in the superiority of one phone system and AT&T adopted the slogan "One Policy, One System, Universal Service" and started buying up smaller companies.
He also promoted the concept that companies should be responsible to the public as well as its shareholders.
AT&T was also known as "Ma Bell" and affectionately called "Mother" by phone phreaks.
By the middle of the 20th century most of the telephone communications in the US was provided by the Bell System, which consisted of:
Original Bell System
AT&T - the Umbrella Company
Long Lines - Long Distance Services
Western Electric - Manufacturing
Bell Laboratories - Research and Development
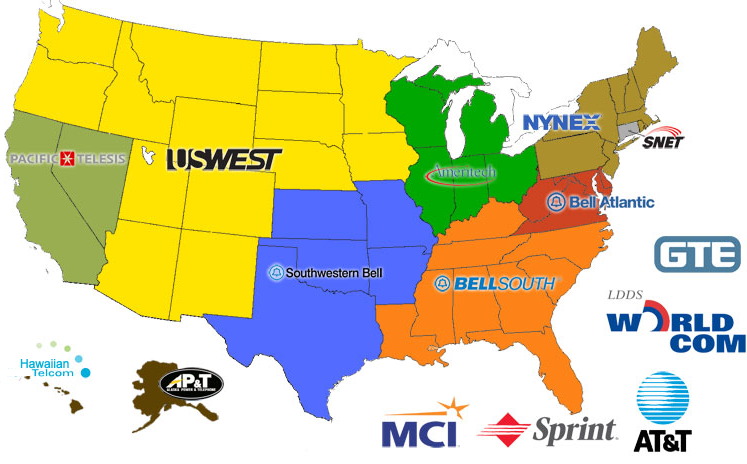
22 Bell Operating Companies - Local Telephone service
Also called Local Exchange Carriers (LECs)
Illinois Bell Telephone Company
Indiana Bell Telephone Company, Incorporated
Michigan Bell Telephone Company
New England Telephone and Telegraph Company
New Jersey Bell Telephone Company
New York Telephone Company
Northwestern Bell Telephone Company
Pacific Northwest Bell Telephone Company
South Central Bell Telephone Company
Southern Bell Telephone and Telegraph Company
Southwestern Bell Telephone Company
The Bell Telephone Company of Pennsylvania
The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Companies (MD, DE, VA, WV)
The Diamond State Telephone Company
The Mountain States Telephone and Telegraph Company
The Ohio Bell Telephone Company
The Pacific Telephone and Telegraph Company
Bell Telephone Company of Nevada (Owned by Pacific Bell)
Wisconsin Telephone Company
There were several Independent Local Exchange Carriers (ILECs)
General Telephone and Electronics (GTE), United Telephone, Southern New England (Connecticut) and many smaller ones.
Universal Service:
The AT&T concept of universal service provided low cost service so almost everyone could afford to have a phone.
The Bell companies subsidized local service with Business Revenes.
Everyone was happy. Businesses needed everyone to have a phone and a phone directory so people could find and contact them.
Competition:
Then companies like MCI and Sprint found they offer lower rates to businesses in metropolitan areas by not having to support large networks for local service.
Bell
In 1974 United States Department of Justice of an antitrust lawsuit against AT&T.
Divestiture:
This led to divestiture in 1984. The AT&T divested the operating companies, which provided local telephone service and kept manufacturing of telephones and switches and long distance service.
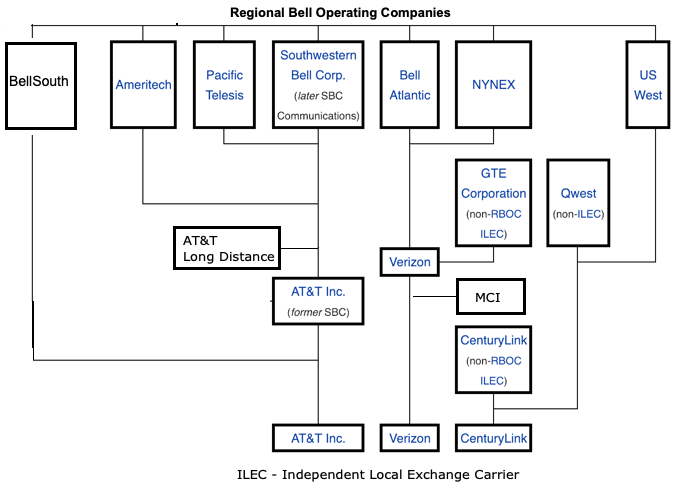
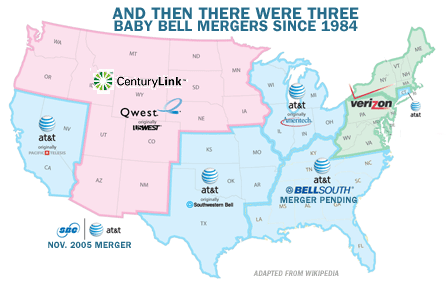
The 22 Bell Operating Companies were consolidated into 7 Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCS) or "Baby Bells"
NYNEX, acquired by Bell Atlantic in 1996, now part of Verizon Communications
Pacific Telesis, acquired by SBC in 1997, now part of AT&T Inc.
Ameritech, acquired by SBC in 1999, now part of AT&T Inc.
Bell Atlantic, merged with GTE in 2000 to form Verizon Communications
Southwestern Bell Corporation, rebranded as SBC Communications in 1995, acquired AT&T Corporation in 2005
BellSouth, acquired by AT&T Inc. in 2006
US West, acquired by Qwest in 2000, which in turn was acquired by CenturyLink in 2011
AT&T retained Long Distance Service
and AT&T Technologies (Western Electric and Bell Laboratories)
The software division of Bell Labs, which provided operating software for the Bell Operating Companies became Bellcore owned byt the 7 RBOCs.
In 1996 AT&T Technologies became Lucent.
At the same time the RBOCs wireless services were merging and spun off.
AT&T and Verizon survived.
Around 2012 AT&T's attempt to buy T-Mobile from Deutsche Telekom was rejected.
1984 breakup of AT&T into 7 Baby Bells and AT&T
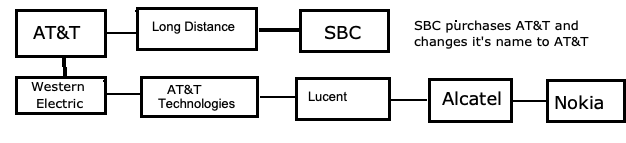
AT&T Evoluton
In 2005, 20 years after the justice department split the telephone business into local and long distance companies they have allowed them to come back together.
SBC was allowed to purchase what was left of AT&T, the Long Distance business, and to change their name to AT&T.
Verizon another local service provider was allowed to purchase MCI a long distance carrier.
This allowed them to compete with the cable TV companies and provide Internet and TV service.
In 2006 manufacturing and research parts of the original AT&T, Lucent, merged with Alcatel SA of France.
In 2016 Alcatel-Lucent was absorbed by Nokia of Finland
See: AT&T Technologies - Wikipedia
What was to become AT&T Wireless was established in 1987 3 years after the breakup. See AT&T Wireless Evolution - Wikipedia
Local telephone service was provided by on of the RBOCs (Regional Bell Operating Companies) depending on where you lived and you had to pick one of the interexchange carriers (IXCs) like AT&T, MCI, and Sprint to provide long distance calls.
Consolidation of Baby Bells
The independent local Exchange Carriers (ILEC's)still remained independent. Two of the larger ones GTE and Southern New England Telephone (SNET) were eventually bought by one of the larger companies. Others still remain. Consolidated Communications an independent company bought a lot of the smaller independent companies. e.g. Roseville Telephone and Elk Grove telephone.
AT&T and Verison wireless businesses are subsidiaries which compete nation-wide with T-mobile, Sprint and other wireless companies.
Terms:
GTE - General Telephone & Electronics
ILEC - Independent Local Exchange Carrier
LEC - Local Exchange Carrier (Bell companies)
MCI - originally Microwave Communications, Inc.
Originally a Long Distance Telephone Carrier
RBOC - Regional Bell Operating Company
SBC - Southern Bell Company (Originally Southwestern Bell - Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas)
Links:
Breakup of the Bell System - Wikipedia
A Brief History of the Rise and Fall of Telephone Competition in the US, 1982-2011
History of telecommunication - Wikipedia
A short history of the telephone industry and regulation
 Technology
Technology
 Telecom
Telecom
 Telephone History - Companies - Bell system
Telephone History - Companies - Bell system
 Technology
Technology
 Telecom
Telecom
 Telephone History - Companies - Bell system
Telephone History - Companies - Bell system