Source: Marjanovic, Lake Tahoe Basin Characterization & Assessment of Exemplary Programs for Water Quality Crediting and Trading Feasibility Analysis, 1989
Also: Truckee River Chronology at nv.gov, Oct, 2011
and Rush, F. Eugene, "Water Resources-Information Series Report 17: Bathymetric Reconnaissance of Lake Tahoe, Nevada and California," Prepared cooperatively by the Geological Survey, U.S. Department of the Interior and the Division of Water Resources, Department of Conservation and Natural Resources, State of Nevada, Carson City, Nevada, 1973.
Mean annual precipitation is 31 in. The middle quartile values are from 21 - 43 in/year.
Assuming runoff is proportional to precipitation this means that about 25% of the time all the water entering the lake would be lost to evaporation, so output to the Truckee River is restricted and the lake level will be lower at the end of the year.
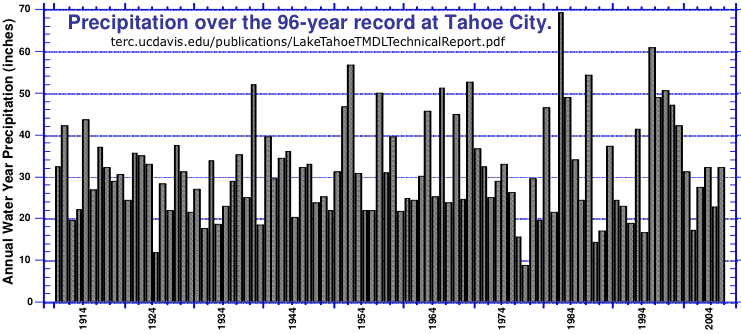
Source: Lake Tahoe Total Maximum Daily Load - Technical Report, (terc.ucdavis.edu/publications/
LakeTahoeTMDLTechnicalReport.pdf), 2007
The capacity of Lake Tahoe id 39 trillion gallons.
Surface area is 122,317 acres (191 sq mi).
The 1935 Truckee River
Agreement, limited the operating range of Lake
Tahoe's surface elevation to between 6,223.0 feet (its
natural rim) and 6,229.1 feet. The dam at Tahoe City is 6 ft high.
Lake levels have fluctuated from 6,220.3 feet (about 3 feet below the rim),
during a prolonged drought in 1992 to 6,229.4 feet (about 0.2 feet above the legal
maximum), during the flood of January 1997.
Outflow to the Truckee River is adjusted to keep the water level within these limits. However, there are minimum flows to supply water for Reno and maximums to avoid flooding in Reno.
See the Truckee River
Because the volume of the lake is so large (156 km3) and its hydraulic residence time so long (about 650 years), its eutrophication may be essentially irreversible.
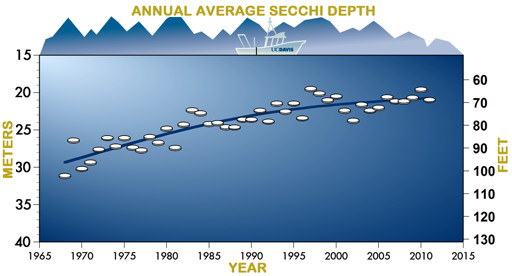
Can be restored to 100' by cutting pollution from runoff, chimney soot, dust and vehicle emissions by 35%
High turbidity areas Emerald Bay and off Tahoe City and South Shore and Incline
Temperature has increased 1/3° from 1969-2006 from global warming.
WHY ARE SHORELINE SCENIC RATINGS DECLINING?
- A dramatic increase in the scale and mass of residential structures
- Structures are placed close to the lake,
- Architectural features have increased visibility
- The unauthorized removal of trees
Restoration Efforts:
In 1969 The Tahoe Regional Planning Agency (TRPA) was created by the United States Congress
It gave TRPA authority to adopt environmental quality standards, called thresholds,
and to enforce ordinances designed to achieve the thresholds.
TRPA has divided the land area in the Lake Tahoe Basin into
three priority watersheds. Priorities are based on many characteristics
including topography, soil erodibility, and soil type, proximity
to streams, etc.
They have established a schedule for implementing Best Management Practices or BMPs for property owners in each of these watersheds.
- paved driveways and parking pads
- infiltration trenches and dry wells
- Gravel under roof drip lines
- adequate vegetative cover and stabilized slopes.
- Stop unnecessary tree removal
Other regulations:
- Elimination of 2-cycle boat engines.
- Changing the boat speed limit in Emerald Bay from 15 MPH to 5 MPH.
- Inspection and registration of boats for emissions and oil/gas leaks.
- Strong erosion-control measures to reduce and/or eliminate runoff
- Organic fertilizers on golf courses and recommended for all lawns and gardens
Guidelines
How can we improve Lake Tahoe's Air Quality?
- Reducing the number of vehicles on the roadways by walking, biking, carpooling, or taking public transit.
- Encouraging all public transit providers to move towards compressed natural gas (CNG) fuels to reduce pollution from buses. TRPA is working with local transit companies to move in this cleaner, greener direction.
As of Aug. 2006 all but two Tahoe Area Regional Transit buses were natural gas powered.
- Installing our Best Management Practices (BMPs) to help reduce wind-blown dust from bare areas and dust caused by driving on dirt driveways.
- Replacing old, non-compliant wood heaters with new, efficient EPA-approved wood or gas heaters and stoves will reduce the smoke in our air, and also the smoke which deposits onto the lake and contributes to the decline in clarity.
The Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board is develop a program, TMDL (Total Maximum Daily Load) (mandated by the Clean Water Act) to limit the flux of nutrients and fine sediment to the Lake. is a water quality restoration plan, mandated by the federal Clean Water Act, designed to reduce the amount of pollution contributing to the decline of Lake Tahoe's clarity.
History:
1861-1901 Clear-cut logging of an estimated 60 percent of the Basin during the Comstock-era
to supply lumber for silver mines in Nevada.
1899 Lake Tahoe Reserve established to address the treatment of the land
1905 became Tahoe National Forest
1910's Effort to make it a National Park failed
1960-1974 Congressional acts passed to resolve controversies over uses of public lands.
Clean Air (1963) and Clean Water Acts (1972), the National Environmental Policy Act (1969).
1969, Tahoe Regional Planning Agency (TRPA) created by the United States Congress
was the first bi-state regional environmental planning agency in the country.
1985 California Attorney General, John Van de Kamp, filed suit in 1985 to prevent TRPA
from granting any further permits for development. Developers were outraged
but lost all of their court appeals.
1950's UC Davis starts studying the basin's ecological problems and their causes.
1990 Tahoe National Forest Plan sets stringent environmental standards
1997 President Clinton and Vice President Gore attend the first annual Lake Tahoe Summit
They announced the Tahoe Restoration Act which authorized $300 million over
10 years for restoration of the Tahoe Basin.
1997 Environmental Improvement Program (EIP) - a coordinated effort designed to protect
and restore Lake Tahoe's natural resources.
The program includes a list of erosion control, land acquisition, watershed,
and forest ecosystem restoration projects.
2000 Congress authorizes $300 million towards restoration of water quality in Lake Tahoe
over a period of 10 years.
2005 The Tahoe Center for Environmental Sciences (TCES) building at Sierra Nevada College in
Incline Village started. Fundraising started in 1994
$13 million in donations, including $2.6 million from the David and Lucile Packard.
UC Davis and Sierra Nevada College.
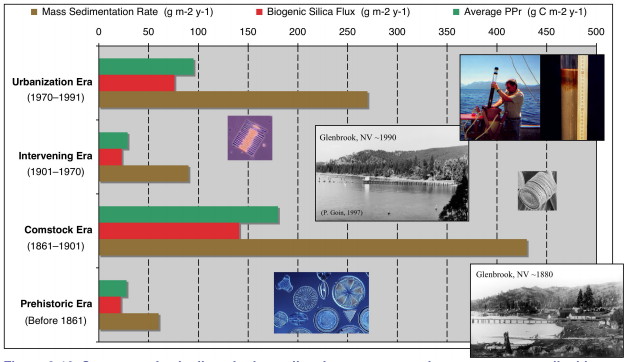
PPr - Primary Productivity - The numeric criterion for algal productivity (mg C/m2/yr.
Source: Tech Report 3-15 2
Groups Solving Problems:
The Federal Interagency Partnership (FIP) and the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency (TRPA) have completed "A Federal Vision for the Environmental Improvement Program at Lake Tahoe" dated June 2006.
TRPA:
Tahoe Regional Planning Agency (TRPA) created in 1969 by the United States Congress
It gave TRPA authority to adopt environmental quality standards, called thresholds,
and to enforce ordinances designed to achieve the thresholds.
TRPA was the first bi-state regional environmental planning agency in the country.
Current TRPA regulations require all homes in the Tahoe Basin to be retrofit with Best Management Practices or BMPs.
See
TRPA Tahoe Area Plans
Tahoe’s future hangs in the balance — again | Reno Gazette Journal March 2023
A March 2023 TRPA governing board will hear a Washoe Board of County Commissioners approved Plan to
ammend The Tahoe Area Plan amendment to allow luxury condominiums in an area originally limited to mixed-use affordable housing and commercial to allow 40 units, already advertised online starting at $2.5 million.
}Area Plan amendment to allow luxury condominiums in an area originally limited to mixed-use affordable housing and commercial.
Backyard Conservation Program at Lake Tahoe is part of a cooperative national program
with the Natural Resources Conservation Service, the National Association of Conservation Districts
and the Wildlife Habitat Council.
The Backyard Conservation Program includes education and outreach activities on proper water and nutrient management, fuel load reduction, defensible space and forest health, proper re-vegetation techniques and plant selection, erosion control and runoff management.
University of California, Davis, Tahoe Environmental Research Center (TERC)
Dedicated to research, education and public outreach on lakes and their surrounding watersheds and airsheds.
League to Save Lake Tahoe (The "Keep Tahoe Blue" people) formed in 1957 is a privately funded, non-profit, public benefit membership organization. Through our Advocacy and Monitoring program, the League acts as the primary watchdog for Lake Tahoe's environment. One of our fundamental goals is to ensure that laws and plans
intended to protect the Lake Tahoe Basin are adequate and effectively enforced. To this end, the League closely monitors the work of the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency.
UC Davis Institute of the Environment at the University of California at Davis (Formerly John Muir Institute of the Environmen)
Tahoe Science Consortium, a membership of research institutions including the University of Nevada - Reno, UC Davis, Sierra Nevada College, Government agencies and others.
UNR Academy for the Environment
NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab with UC Davis have installed a network of research and monitoring buoys on Lake Tahoe.
Tahoe Integrated Information Management System (TIIMS) is a bi-state, multi-agency information management system developed to house and disseminate wide-ranging information about Lake Tahoe Basin planning and restoration efforts via the Internet.
Tahoe Resource Conservation District (TRCD) and the Natural Resources Conservation Service
(USDA/NRCS), working with their many partners, will protect
and enhance the water quality of Lake Tahoe through reduction
of impacts associated with the development and management
of private residences in the Basin.
California Tahoe Conservancy - The Conservancy is an independent State agency within the Resources Agency of the State of California. It was established to develop and implement programs through acquisitions and site improvements to improve water quality in Lake Tahoe, preserve the scenic beauty and recreational opportunities of the region, provide public access, preserve wildlife habitat areas, and manage and restore lands to protect the natural environment.
Tahoe Interagency Monitoring Program (LTIMP) created to acquire and disseminate the water quality information necessary to support science-based environmental planning and decision making in the basin. The LTIMP is a cooperative program with support from 12 federal and state agencies with interests in the Tahoe Basin.
Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board - The mission of the RWQCBs is to develop and enforce water quality objectives and implementation plans which will best protect the beneficial uses of the State's waters, recognizing local differences in climate, topography, geology and hydrology. Lahontan works to preserve and enhance the quality of California's water resources and ensure their proper allocation and efficient use for the benefit of present and future generations.
1. Eutrophication is the enrichment of an ecosystem with chemical nutrients, typically compounds containing nitrogen or phosphorus. Eutrophication is considered a form of pollution because it promotes plant growth, favoring certain species over others and forcing a change in species composition.
The Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
has several national programs to provide technical and financial assistance for
conservation and restoration projects on private lands. These programs include the
Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP), the Wetland Reserve Program
(WRP), and the Wildlife Habitat Incentives Program (WHIP).
Links:
2. Lake Tahoe Total Maximum Daily Load - Technical Report, (terc.ucdavis.edu/publications/
LakeTahoeTMDLTechnicalReport.pdf), 2007 by
The California Regional Water Quality Control Board, Lahontan Region
The Nevada Department of Environmental Protection.
and UC Davis, Tahoe Environmental Research Center
Tahoe Facts
Lake Tahoe Basin Characterization & Assessment of Exemplary Programs for Water Quality Crediting and Trading Feasibility Analysis, Marjanovic 1989
Truckee River Operating Agreement, U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, January, 2008
Includes "Truckee River Riparian Vegetation and Fluvial Geomorphology Study", U.S. Fish and WIldlife Service, Sept., 1993
Executive Summary
Truckee River Chronology at nv.gov, Oct, 2011
Tahoe Center for a Sustainable Future (TCSF)
Independence Lake acquired by The Nature Conservancy and the Truckee Donner Land Trust in April 2010
Truckee Donner Land Trust (tdlandtrust.org)
Plan that would allow many more piers, buoys and slips has critics concerned, LA Times, Feb. 21, 2007
Progress Report Federal Actions At Lake Tahoe, 2002
Tahoe Donner Development
last updated 25 June 2012
West Shore Info | Ski Info | Directions | Homewood Map.
| 
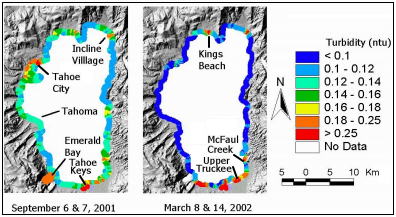 A study by Taylor et al. (2003) explored near shore clarity by collecting field
measurements of turbidity in (NTU - nephelometric turbidity units) between September 2001 and August 2003. The study
showed moderate to extremely elevated near-shore turbidity in the south shore area.
Specifically, the mouth of the Upper Truckee River was characterized as having
extremely elevated turbidity, while the Al Tahoe intervening zone, Bijou Creek, Tahoe
Keys Marina and Ski Run Marina showed moderate levels of turbidity. 2
A study by Taylor et al. (2003) explored near shore clarity by collecting field
measurements of turbidity in (NTU - nephelometric turbidity units) between September 2001 and August 2003. The study
showed moderate to extremely elevated near-shore turbidity in the south shore area.
Specifically, the mouth of the Upper Truckee River was characterized as having
extremely elevated turbidity, while the Al Tahoe intervening zone, Bijou Creek, Tahoe
Keys Marina and Ski Run Marina showed moderate levels of turbidity. 2

