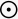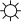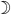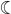- absolute magnitude (Ho):
- The brightness of a comet when it is at 1 AU from both the Earth and Sun. As this virtually never happens, this quantity is calculated from the comet's light curve. Unfortunately, this quantity is far from absolute. It can be different pre- and post-perihelion. It can also change from apparition to apparition (for periodic comets).
- Asteroid:
- Like a small planet from 1 to 600 mi. (1/4 the size of our moon) in diameter. Composed of rock, irridium, carbon or metal.
- astronomical unit (AU):
- Standard unit for measuring distance within the solar system. One AU is equal to the average distance between the Sun and Earth or about 93 million miles.
- Comet:
- A relatively small, sometimes active object, which is composed of dirt and ices. Comets are characterised by dust and gas tails pointing away from the sun when in proximity to the Sun. Far from the Sun it is difficult to distinguish an asteroid from a comet.
- Ecliptic:
-
- Equinox:
-
The time when the Sun is directly above the Earth's equator, occurring around March 20-21 and September 22-23 each year. On these dates, night and day are nearly of the same length. See note1 below.
See also: Solstice
- LINEAR:
- Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research team.
- Meteoroid:
- A small ( smaller than 1 mile across) particle from an asteroid or comet orbiting he Sun.
- Meteor:
- A meteoroid that is observed as it burns up in the Earth's atmosphere - a shooting star.
- Meteorite:
- A meteoroid that survives its passage through the Earth's atmosphere and impacts the Earth's surface.
- NEAT:
- Near Earth Asteroid Tracking program.
- perihelion:
- The point in a comet's orbit that it is closest to the Sun.
- SOHO:
- Solar & Heliospheric Observatory. Joint venture with NASA and
and the European Space Agency (ESA) to study the sun.
- Solstice:
-
The time when when the Earth's axis tilts the most toward or away from the Sun, causing the Sun to be farthest north or south at noon. They occur around June 20-21 and December 21-22 each year. The start of winter or summer.
See also: Equinox
- α: Right ascension R.A.
- Longitude in the celestial equatorial coordinate system. Measured measured from 0 to 24 hours toward the east.
- δ: Declination
- Latitude in the celestial equatorial coordinate system. Measured +90° to the north or -90° to the south.
- β: Ecliptic latitude
- Latitude in the celestial ecliptic coordinate system. Measured +90° to the north or -90° to the south.
- λ: Ecliptic longitude or celestial longitude
- Measured from this point on 0° to 360° towards the east
from a fixed point known as the first point of Aries or the vernal equinox. See note1 below.
See The Ecliptic coordinate system for conversion from α,δ to/from λ,β
- Zodiac:
- Solar Zodiac - The thirteen signs / constellations against which the Sun is seen to move, as seen from the Earth.
Planetary Zodiac- A band of the heavens approximately 34¡ wide,
centered on the Ecliptic, against which the planets are seen to move, as seen from the Earth.
Lunar - Lunar or Draconic Zodiac is a band of the heavens approximately 10¡ wide,
centered on the ecliptic, against which the Moon is seen to move, as seen from the Earth
Glossaries at IMO.
Astronomical symbols:
|
Sun -   | Waxing Crescent - 
Waining Crescent (decrescent)- 
|
Mercury -  Mercury's winged helmet and caduceus
Venus - ♀ Venus's hand mirror
Earth - Mercury's winged helmet and caduceus
Venus - ♀ Venus's hand mirror
Earth -  Globe with equator and meridian
Mars - ♂ Mars's shield and spear Globe with equator and meridian
Mars - ♂ Mars's shield and spear
|
Jupiter -  Jupiter's thunderbolt or eagle
Saturn - Jupiter's thunderbolt or eagle
Saturn -  Saturn's sickle or scythe
Uranus - Saturn's sickle or scythe
Uranus - 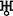 , ,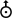 Neptune -
Neptune - 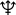 Neptune's trident
Pluto - Neptune's trident
Pluto - 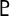 , , 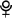
|
|
Sign/
Constellation | Trans-
lation | Sym-
bol | λ |
| Aries | Ram | 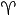 | 0° |
| Taurus | Bull | 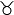 | 30° |
| Gemini | Twins | 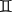 | 60° |
| Cancer | Crab |  | 90° |
| Leo | Lion |  | 120° |
| Virgo | Maiden |  | 150° |
|
| Libra | Balance |  | 180° |
| Scorpius | Scorpion | 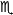 | 210° |
Serpens/
Ophiuchus * | serpent
bearer | 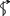 | |
| Sagittarius | Archer | 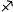 | 240° |
| Capricornus | Sea Goat | 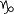 | 270° |
| Aquarius | Water Bearer |  | 300° |
| Pisces | Fish |  | 330° |
|
|
* The two part constellation, Serpens-Ophiuchus, is intersected by the ecliptic but is not considered part of the zodiac.
Note 1: The zodiac in astrology are sun signs, when the sun is in the constellation, or 6 months from the time is is overhead (opposite the sun) in the night sky. Around 2000 years ago,
the Sun was in the constellation of Aries at the spring equinox.
The Vernal Equinox occurs nowadays
when the Sun is in the constellation of Pisces. The equinoxes regress along the ecliptic at 50.35" per year. See Precession at
See Also:
Astronomical Symbols at Wikipedia and Symbols for moons
Glossary of Astronomy Terms - Astronomy Reference Guide on Sea and Sky
Return to Astronmy
last updated 11 June 2014
|
 Science
Science
 Astronomy
Astronomy

 Science
Science
 Astronomy
Astronomy