
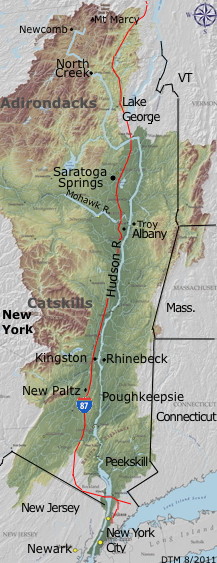
 The 315 mile long river, which flows from through the eastern new York state was earlier known as the Muhhekunnetuk which means "the river that flows both ways" and the Great Mohegan by the Iroquois. It rises at Lake of the Clouds Tear, on the slopes of Mount Marcy, where the Opalescent River and Twin Brooks form the headwaters in the Adirondack Mountains, flows past Albany, and finally forms the border between New York City and New Jersey at its mouth before emptying into Upper New York Bay.
The 315 mile long river, which flows from through the eastern new York state was earlier known as the Muhhekunnetuk which means "the river that flows both ways" and the Great Mohegan by the Iroquois. It rises at Lake of the Clouds Tear, on the slopes of Mount Marcy, where the Opalescent River and Twin Brooks form the headwaters in the Adirondack Mountains, flows past Albany, and finally forms the border between New York City and New Jersey at its mouth before emptying into Upper New York Bay.
The Hudson is often mistaken for one of the largest rivers in the United States, but it is an estuary throughout most of its length below Troy and thus only a small fraction of fresh water, about 15,000 cubic feet per second, is present.
The strong tides of the lower Hudson River which is also known as a tidal estuary makes parts of New York Harbor difficult to sail Depending upon the tides the ice flows from south to north during winter.


 History:
History:1609 - Henry Hudson, an Englishman sailing for the Dutch East India Company, sailed the Half Moon up the North River (later renamed for him) in search of the Northwest Passage.
1825 - The Erie Canal is completed connecting Lake Erie to the Hudson just above Albany to facilitate transport of goods between the Great Lakes and New York City.
1828 - The Delaware and Hudson Canal ended at the Hudson at Kingston, running southwest to the coal fields of northeastern Pennsylvania.
Poster of this picture at Zazzle.com
 Death of the River:
Death of the River:
Back in the mid-sixties, after centuries of accumulated sewage pollution and industrial dumping of toxic chemicals, the Hudson River, like many of America's most important estuaries, was declared "dead". The river's fragile ecological system was devastated. Not a single fish was found in many areas, and the level of commercial fishing had dropped so dramatically as to be regarded as nonexistent.
The modern Environmental movement, which began in the 1960s with concern about air and water pollution spawned several efforts to clean up the river.
- 1966 Pete Seeger and a small group of river-lovers built a boat to dramatize the river's plight.
- 1966 The Hudson River Fishermen's Association (HRFA) formed for the same purpose.
- 1972 Federal Clean Water Act
- 1990 HRFA becomes the Riverkeeper and a group of attorneys lead by Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. start prosecuting poluters.
Sloop Clearwater
 Recognizing this incredible social and environmental tragedy, Pete Seeger, a popular musician and respected activist, decided "to build a boat to save the river". Holding small, fundraising river concerts throughout the Hudson River Valley, he literally passed his banjo among the crowd, collecting contributions to build the elegant tall ship that would become a symbol of environmental advocacy, the flagship of the American Environmental Movement, the sloop Clearwater.
Recognizing this incredible social and environmental tragedy, Pete Seeger, a popular musician and respected activist, decided "to build a boat to save the river". Holding small, fundraising river concerts throughout the Hudson River Valley, he literally passed his banjo among the crowd, collecting contributions to build the elegant tall ship that would become a symbol of environmental advocacy, the flagship of the American Environmental Movement, the sloop Clearwater.
Riverkeeper
Riverkeeper is a member-supported watchdog organization dedicated to defending the Hudson River and its tributaries and protecting the drinking water supply of nine million New York City and Hudson Valley residents.
Riverkeeper began as the Hudson River Fishermen's Association (HRFA) in 1966.
The landmark passage of the Clean Water Act (CWA) in 1972 made it illegal to discharge pollutants, whether liquids or solids, into waterways without permits.
In 1983 the HRFA launched a patrol boat, and hired John Cronin as the first full-time Hudson Riverkeeper, creating a Riverkeeper organization based on his work. The HRFA changed its name to Riverkeeper in 1986.
 In 1990, Riverkeeper's Chief Prosecuting Attorney, Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., and a team of Riverkeeper attorneys took on
rapacious developers and lackluster enforcement agencies in what has become an ongoing battle to halt the degradation
of the reservoirs and streams that constitute the water supply for nine million New York City and Westchester County
residents.
In 1990, Riverkeeper's Chief Prosecuting Attorney, Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., and a team of Riverkeeper attorneys took on
rapacious developers and lackluster enforcement agencies in what has become an ongoing battle to halt the degradation
of the reservoirs and streams that constitute the water supply for nine million New York City and Westchester County
residents.
Riverkeeper has successfully challenged the illegal activities of some of the largest and most notorious polluters, including: Exxon-Mobil, General Electric, Consolidated Edison, Metropolitan Transit Authority, the City of New York, and the New York State Department of Transportation.
In addition to his role with Riverkeeper, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. serves as Chairman of Waterkeeper Alliance, a global movement of 190 Waterkeeper organizations.
In 2005 Kennedy accepted the Sierra Clubs William O. Douglas Award on behalf of the Riverkeepers. Transcript of acceptance speech.
In 2010 Mr. Kennedy was named one of Time magazine's "Heroes for the Planet" for his success helping Riverkeeper lead the fight to restore the Hudson River.
See The Riverkeeper Story (pdf).
Maps:
Hudson Valley
Catskills
Adirondacks
Orange and Rockland Counties
Bergen and Westchester Counties
New York City
Links:
Riverkeeper - NY's Clean Water Advocate
Riverkeeper Boat Blog: August 2009
Hudson River Sloop Clearwater
Music
Clearwater's Great Hudson River Revival
Riverkeeper report: Hudson River users have 21% chance to encounter sewage | The Journal News | LoHud.com
Hudson River Basin Study Unit at the USGS
State of the Hudson: River revival only part of the way
Hudson River at the Altius Directory
Return to Places