Under Construction 
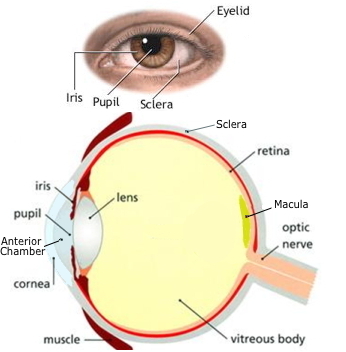
- Iris - A flat and ring-shaped membrane behind the cornea of the eye with an adjustable circular opening in the center called a pupil. It regulates the amount of light that gets into the eye, shrinking (pupil gets bigger) to let in more light in low light situations.
- Pupil - The area in the center of the iris where light passes into the eye.
- Sclera - The white of the eye. Opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye covering all of the eyeball but the cornea.
- Eyelid - Flap of skin which covers the eye when your blink or close your eyes.
- Cornea - The transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber.
- Anterior chamber - The fluid-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface filled with aqueous humor.
- Vitreous - The clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina gives the eyeball it's shape. As the vitreous shrinks over time, it becomes somewhat stringy, and the strands can cast tiny shadows on the retina called floaters.
- Retina - A layer at the back of the eyeball containing cells that are sensitive to light and that trigger nerve impulses that pass via the optic nerve to the brain. It is composed of light sensitive cells known as rods and cones.
- Macula - A 1/4 inch diameter pigmented area at the center of the retina that is extra sensitive. It gives us the ability to see “20/20” and provides the best color vision.
- Optic nerve - A collection of retinal ganglion cell axons (part of a neuron) connecting the light sensing cells in retna to the brain.
Eye Conditions - Diseases:
- Near sightedness
- Far sightedness
- Stigmatism
- Floaters
- Detached Retina
Symptoms: Flashes of light
Seeing lots of new "floaters" (small flecks or threads)
Darkening of your peripheral (side) vision
Problem: Retina is detached from its underlying tissue
Treatment: Laser (thermal) or freezing (cryopexy)
- Age Related
- Age Related Macular Deterioration (ARMD)
Symptoms: Loss of central vision
Difficulty reading or performing tasks that require detail
Distorted vision (Straight lines such as doorways or edges of windows may appear wavy or bent.
Problem: Macula breaks down slowly
Treatment: No proven medical therapy for dry macular degeneration.
In selected cases of wet MD, laser photocoagulation is effective for sealing leaking or bleeding vessels.
- Cataracts
Symptoms: hazy, blurry vision and sensitivity to glare.
Problem: Clouding of lens
Treatment: Replacement with artificial lens
- Glaucoma
Symptoms: None
Get pressure test regularly after the age of 40
Problem:Fluid builds up in the eye, increasing the internal pressure and eventually damaging the optic nerve
Treatment: Eye drops to reduce pressure
Laser surgery
Medication
- Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD) -A natural change that occurs during adulthood, when the vitreous gel that fills the eye separates from the retina
- Diabetic retinopathy
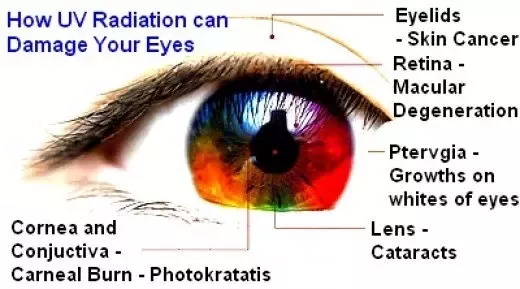
Looking at the Sun:
Permanent damage to the retina has been shown to occur in as little as a minute and a half.
See Looking at the sum and viewing an eclipse.
Links:
Cataracts,Glaucoma,Macula Degeneration,Diagnostic Eyecare
How long do you need to look at the sun to damage your eyes? - Quora
Products:
Age-Related Eye Diseases | Cataracts | Glaucoma - Consumer Reports
Eyeglasses
Sunglasses
Return to Health
last updated 13 Aug 2017
|
 Health
Health
 Eyes
Eyes
 Health
Health
 Eyes
Eyes

